Surgery
Introduction to Surgery
GNU Health allows you to document all surgical procedures performed per patient and in a health institution overall. It uses the ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) of the World Health Organization (WHO) to identify the type of surgery.
ICD-10-PCS
The ICD-10 Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) is a World Health Organization medical classification used for procedural codes. When procedures are performed for specific diseases or disorders, the disease or disorder is not contained in the procedure code. There are no codes for procedures exclusive to aneurysms, cleft lip, strictures, neoplasms, hernias, etc. The diagnosis codes, not the procedure codes, specify the disease or disorder.
Surgeries per Patient
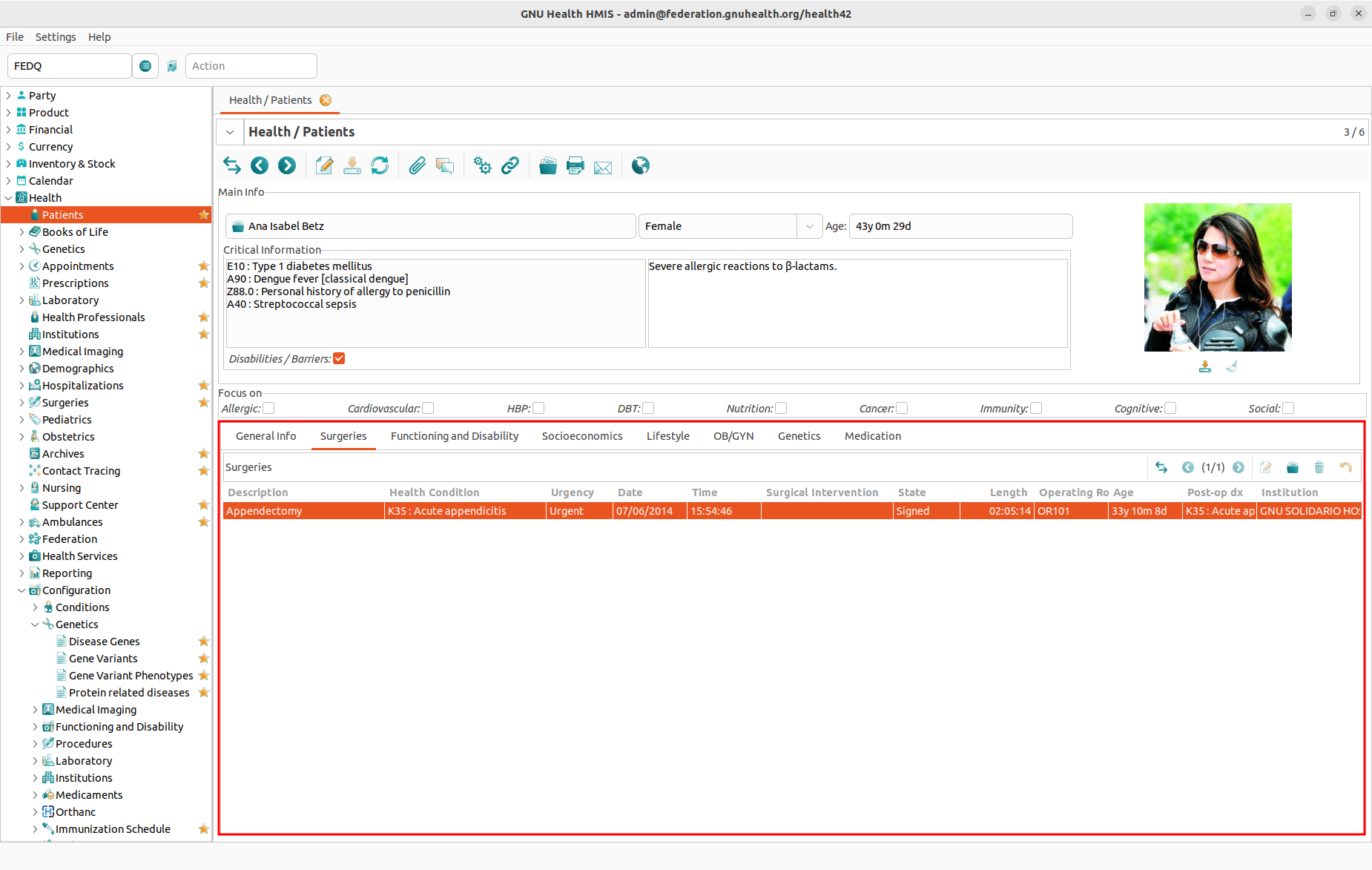
To view and edit the surgeries of a specific patient, open the Patients form and switch to the Surgeries tab in the lower half of the form. There you will find a list of all surgical procedures this patient had (if any).
The list view provides the following information:
Description
Base Condition
Urgency
Date (including Time)
Duration
Operation Room
Age of the patient at the time of the surgery
Institution
To see the full record, double click on a list entry. This will bring up the Surgery form (see below).
To add a new Surgeries record, click the Relate button from the toolbar and choose Surgeries. This will open the list in a new window where you are able to add new records.
All Surgeries
In the Health → Surgeries section you will find a list of all surgeries in the system. This is the way to look for a surgery when you don’t know the name of the patient, and it allows you to get a broader picture of what is going on in the operation room.
The columns of that list are the same as in the Patients form (see above). To see the full record, double click on a list entry. This will bring up the Surgery form (see below).
Surgeries Form
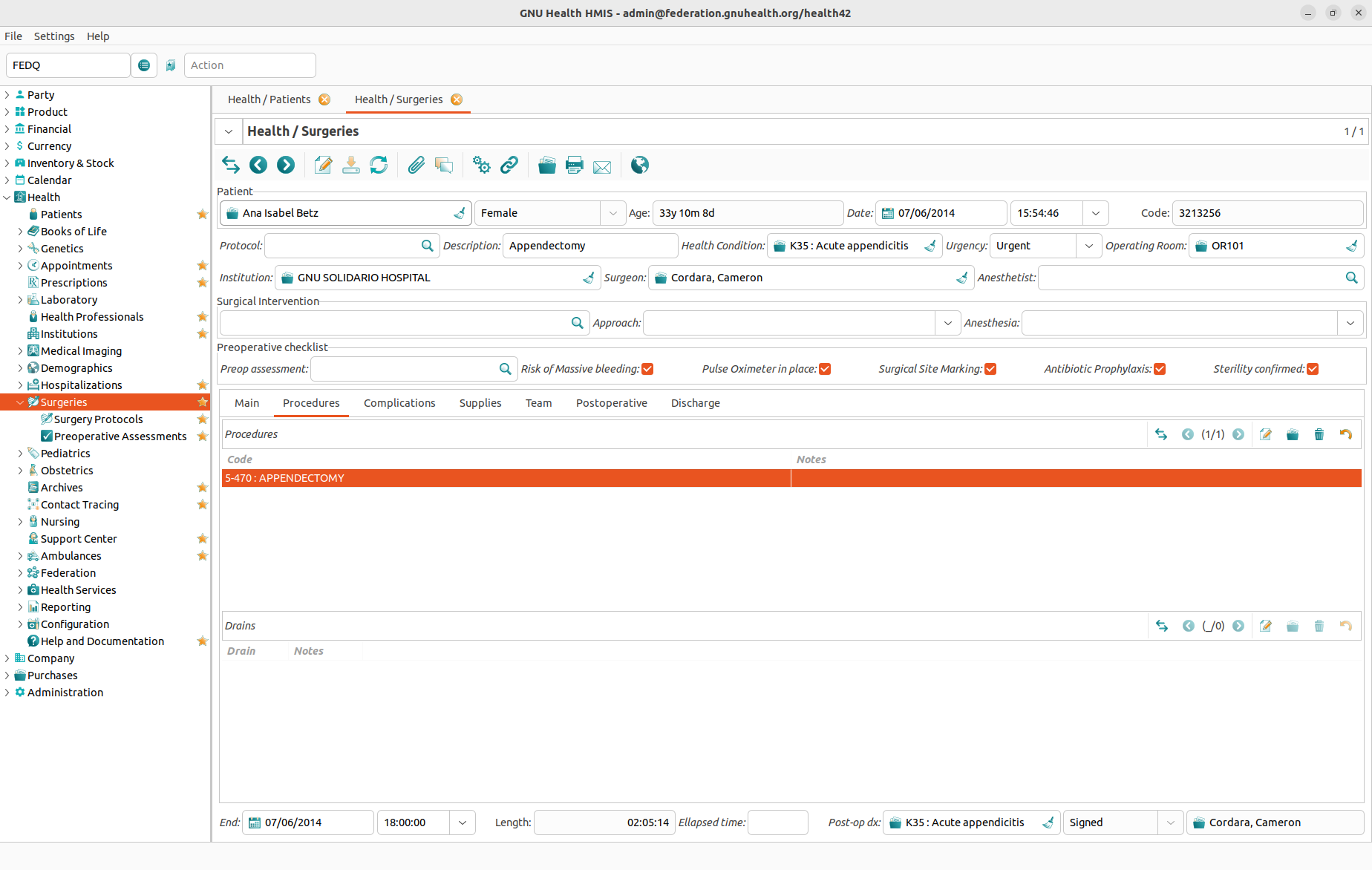
For every surgery you can store the following information:
Patient: Link to a Patient record.
Date (including time)
Age of the patient at the time of the surgery: Calculated based on the date of birth and the date of the surgery.
Code
Description
Base Condition: Link to a Diseases record.
Urgency: Choose between “Optional”, “Required”, “Urgent”, or “Emergency”.
Operating Room: Link to an Operating Room record (see Health Institutions: Operating Rooms).
Surgeon: Link to the health professional who was responsible for the surgery.
Anesthesist: Link to the health professional who was responsible for the anesthesia.
Patient Surgical Risk Assessment section:
ASA PS: Choose between “PS1: Normal healthy patient”, “PS2: Patients with mild systemic disease”, “PS3: Patients with severe systemic disease”, “PS4: Patients with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life”, “PS5: Moribund patients who are not expeted to survive without the operation”, or “PS6: A declared brain-dead patient who organs are removed for donor purposes”.
RCRI: See section “Revised Cardiac Risk Index” below.
Mallampati Score: In anesthesia, the Mallampati score is used to predict the ease of intubation. It is determined by looking at the anatomy of the oral cavity. A higher Mallampati score is associated with more difficult intubation as well as a higher incidence of sleep apnea. Choose between “Class 1”, “Class 2”, “Class 3”, or “Class 4”.
Preoperative Checklist section:
Risk of Massive Bleeding: Check if appropriate
Pulse Oximeter in Place: Check if appropriate
Surgical Site Marking: Check if appropriate
Antibiotic Prophylaxis: Check if appropriate
Sterility Confirmed: Check if appropriate
Procedures section: As we can see in the screenshot, GNU Health helps you searching the procedure using a filter with two different categories, code and long text.
Code
Notes
Details / Incidents
Anesthesia
End
Duration
State: As long as the record is not signed, the state is “In progress”. As soon as you click the Sign button, the state will change to “Done”.
Signed by: As soon as the record is signed it will show the name of the signing health professional where the Sign button was.
Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI)
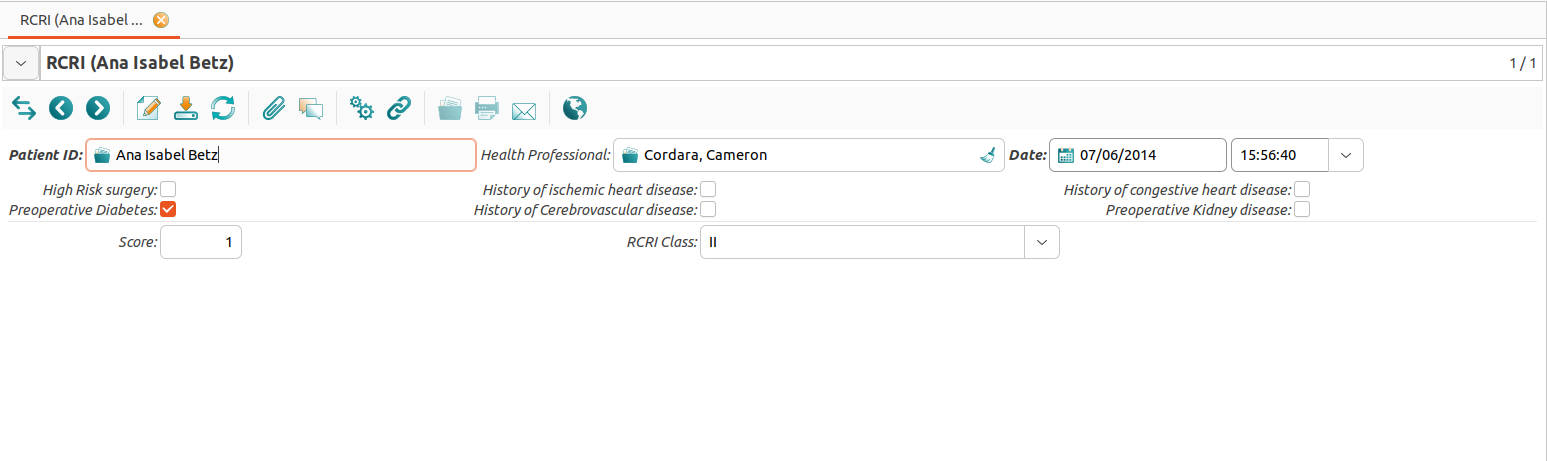
The Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI) is a method to indicate a patient’s risk for perioperative cardiac complications. The RCRI Score and Class are entered via a dialog which allows you to indicate the following risk factors:
High Risk Surgery
Preoperative Diabetes
History of Ischemic Heart Disease
History of Cerebrovascular Heart Disease
History of Congestive Heart Disease
Preoperative Kidney Disease
Based on this data, GNU Health automatically calculates the Score (0 .. 6) and the RCRI Class (I .. IV).