Neglected Tropical Diseases
Introduction to Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTD) are a group of infections which are common in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are medically diverse in terms of pathogens, prevention measures, and treatments. Compared to the big three diseases targeted by the UN Millennium Development Goal No. 6 (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), NTDs get less funding for treatment and research. The World Health Organisation (WHO) has prioritized 17 neglected tropical diseases which are common in almost 150 countries, affecting more than 1.4 billion people. (Read more about neglected tropical diseases.)
Note: To use the functionality described in this chapter you must have the modules health_ntd, health_ntd_chagas, and health_ntd_dengue installed. (Modules)
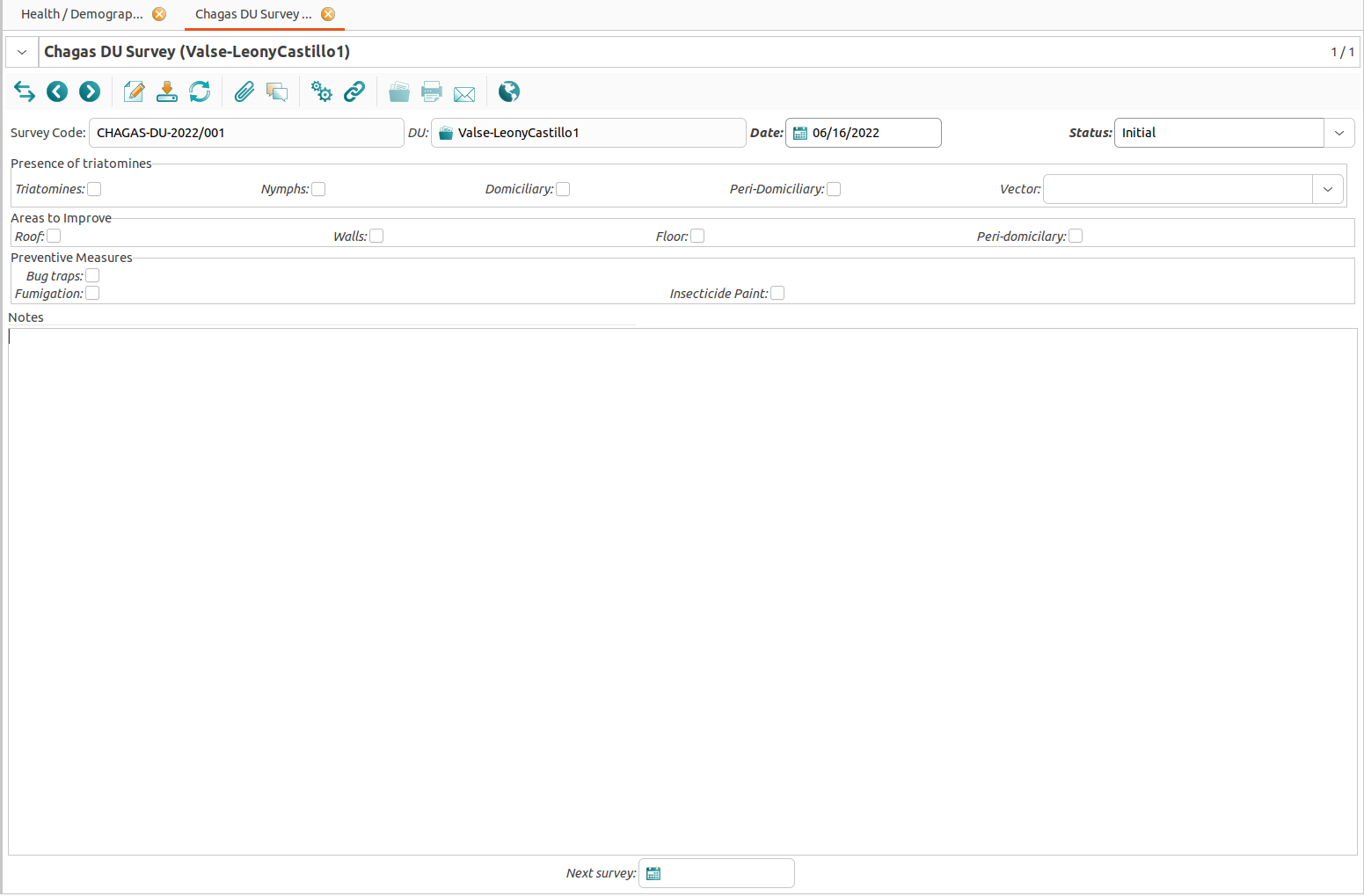
Chagas Disease
The Chagas disease is caused by a protozoa and spread by contact with infected feces of the triatomine bug. The protozoan can enter the body via the bug’s bite, skin breaks, or mucous membranes. Infection can result from eating infected food and coming into contact with contaminated bodily fluids. There are approximately 15 million people infected with Chagas disease. The chance of morbidity is higher for immuno-compromised individuals, children, and elderly, but very low if treated early. The Chagas disease can be diagnosed through a serological test (although the test is not very accurate) and treated etiologically or with drugs (although the drugs have severe side effects). (Read more about Chagas disease.)
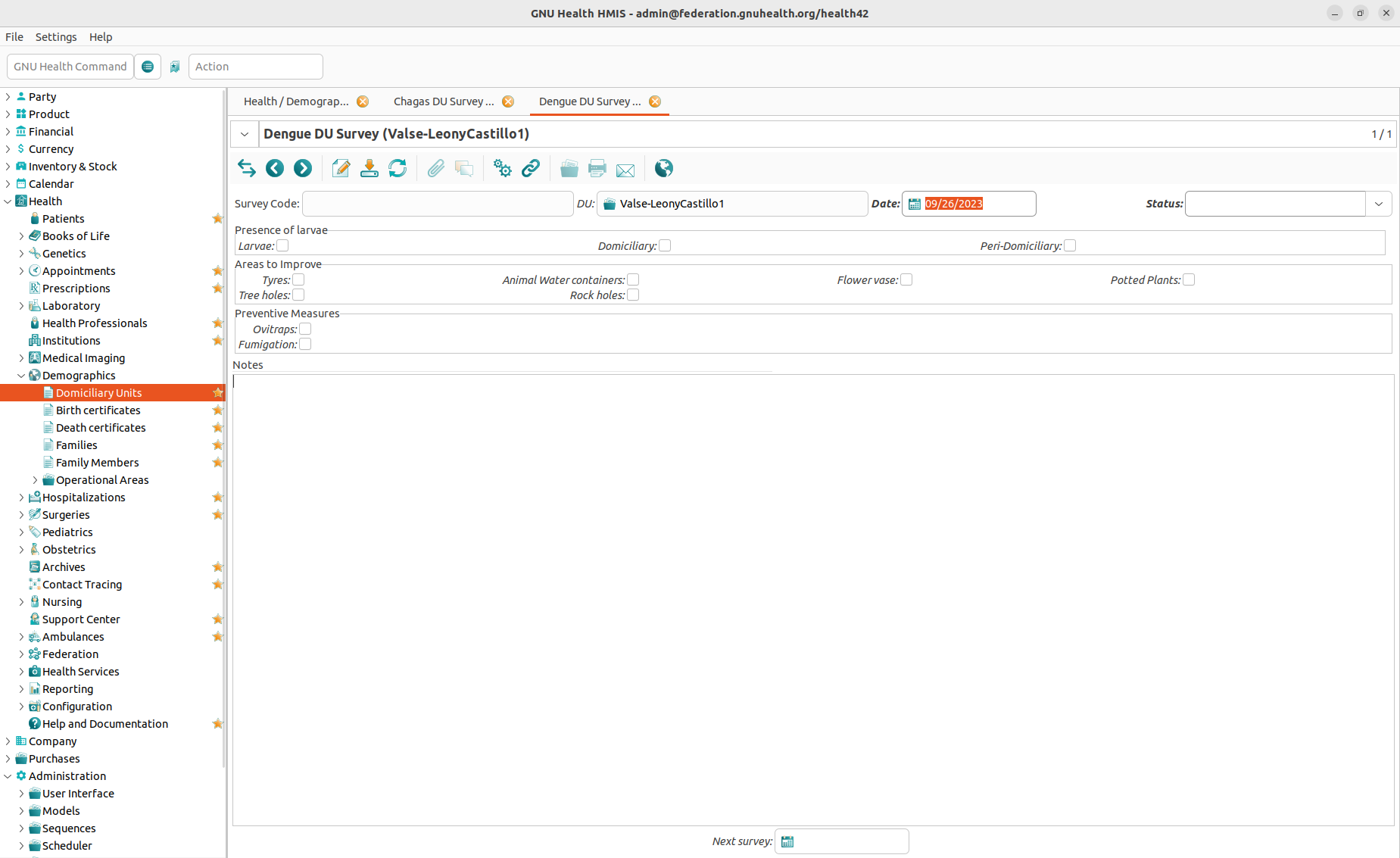
Dengue Fever
Dengue fever is caused by a virus transmitted via mosquito bites. The fever is usually not fatal, but infection with one of four serotypes can increase later susceptibility to other serotypes, resulting in a potentially fatal disease called severe Dengue. There are 50–100 million dengue fever infections annually in Asia, Latin America, and Northern Australia. No treatment for either Dengue or severe Dengue exists beyond palliative care. (Learn more about dengue fever.)