Configuration
The Configuration Section in GNU Health
In most databases – and GNU Health is no different here – there are two categories of data: Some data is created and updated permanently, while other data, once entered into the system, remains quite static. For example, during a working day in a hospital many new patients, evaluations, prescriptions and hospitalizations are stored in GNU Health. On the other hand, the staff of health professionals, the medicaments available in the pharmacy, the medical procedures provided or the hospital infrastructure (buildings, beds, operating rooms) will not change very much during a day, a week or even a month.
The second type of data is grouped in the Health → Configuration section, and this chapter provides an overview for this section. Since most configuration options are easier to understand in their context, you won’t find too many details here but links to other chapters of this book where data from the Configuration section will be used.
Notes:
The subsections available under the Health → Configuration section will vary depending on the modules installed in your system. This chapter describes the configuration options whith all GNU Health modules installed.
There are configuration options on a more technical level too, relevant only to system administrators. These are not covered in this chapters since they are not part of the Health → Configuration section.
Diseases
Todo
Add Basics - Configuration - Diseases
Genetics
In the Genetics subsection you define genetic traits of diseases and thair variants. Configuration can be done in four submenus:
Desease Genes (genetic traits of diseases) *Natural Variants (map a phenotype to a variant of a disease) *Variant Phenotypes (configure the phenotype for variant) *Protein related diseases (cofigure traits and information of diseases) For this configuration option to show the *health_genetics module must be activated in the Andministration section.
Imaging
In the Medical Imaging subsection you can define imaging types and create different imaging studys. For this configuration option to show the health_imaging module must be activated in the Andministration section.
Procedures
In the Procedures subsection you define procedures as a text and map it to a code for reference.
Laboratory
In the Laboratory subsection you define the Lab Test Types, i.e. all tests a laboratory can provide, including all parameters to be analyzed during that test. You can also configure the Lab Test Units used in the laboratory. For this configuration option to show the health_lab module must be activated in the Andministration section.
Note
For more details, please refer to the Laboratory chapter.
Institutions
In the Institutions subsection you define the organisational structure and physical assets of your health institution. This includes the following data:
Buildings
Units
Wards
Beds
Operation Rooms
Note
For more details, please refer to the Health Institutions chapter.
People
To create People, that represent any given person in the system follow Party->Parties->People. Ceating a new entry or double clicking on an entry, will lead you to the form with all the basic information about the person.
To create a person some fields are manditory to fill out:
Name: Given or chosen names.
Family names: names usualy inherited from the parents or legal partner.
PUID: identifier in the system.
(The entry can also be marked as Active to be accessible in other views.)
Within this form some field of the health tab are manditory:
DoB: Date of Birth. (Age is automaticaly calculated.)
Gender: Social and cultural related internal identity differentiated of biological sex.
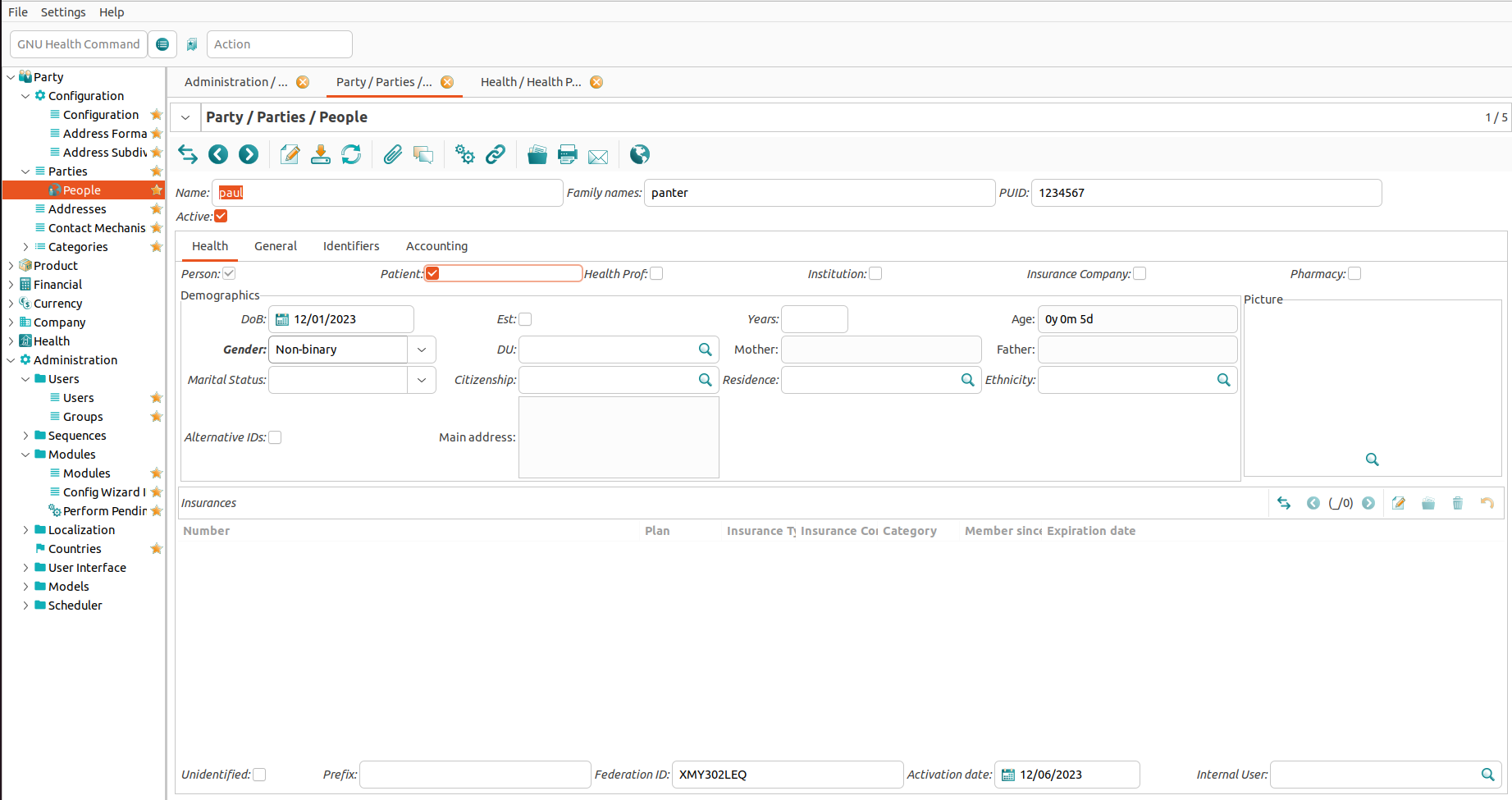
People can have any combination of atributes checkt of being a:
Person
Patient
Health professional
Insurance
Institution
Pharmacy
Those atributes are inherited from Party. (Example: For a Person only Patient and Health Professional are usefull combinations.)
There are different tabs int the form, being:
Health: Basic information of the person.
General: Additional general information like workplace or school.
Identifiers: Names ore Ids to identify the person.
Accounting: Personal Accounting information.
Health Professionals
In the Health Professionals subsection you manage the staff of a health institution. A Health Professionals record contains mainly the professional qualifications, while the personal information (like name, date of birth, home address and so on) is stored in the associated Party record. The following fields are available in a Health Professionals record:
Health Professional: Link to a Party record. You can either select an existing record or create a new one. (Please note that only party records with the Health Professional flag can be found when searching. So if you can’t find a party that exists already in your system, please check this flag before unintentionally creating a duplicate record.)
Licence ID
Specialities: One or more Health Professional Specialites that health professional has experience in. You can select from the list of existing specialities (which will be the standard procedure) or create a new one if necessary.
Extra Info
Institution: Link to a Health Institution record.
Main Specialty: Link to one of the entries in the Specialties list of this health professional (see above). Please note that you must save the Health Professionals record first for being able to edit this field.
PUID: Identifier from the Party record. Filled in automatically.
Note: In GNU Health, one health professional can only work for one health institution at a time. If you try to create a second Health Professionals record linking to the same Party record, you will get an error message.
Note
For more details, please refer to the Health Professionals chapter.
Medicaments
In the Medicaments you can create and configure different kinds of medication. The Medicaments view in the Medicaments can be used to configure or create a medicament. To configure the traits wich define the Medicament can be configured in the following views:
Medication Frequencies define intervals between medication
Drug Dose Units configure units used for medication
Drug Administration Routes configure possible ways to take medicine
Drug Forms configure the kinds of medicine: pills, enema, lotion, etc.
Medicament categories configure categorization
Immunization Schedule
In the Immunisation Schedule subsection you can configure vaccine schedules and doses.
Misc
Here you can find more configuration options. Those are commands, different traits used for some forms and entities as well as the cofiguration of insurances.
Occupations
Configure a list of occupations a patient can have.
Ethnicities
Configure a list of Ethicities.
Medical Specialities
Configure a list of medical fields a health proffessional can specialize in.
Recreational Drugs
Todo
Add Basics - Configuration - Recreational Drugs
Pediatrics Growth Charts WHO
Todo
Add Basics - Configuration - Pediatric Growth Charts WHO
Insurances
In this subsection within Misc you can configure insurance companies and insurance plans in three configuration views:
Insurances
Insurance Plans
Insurance Company