1. Overview
Note
This is a community effort which is external to the official HIS package!
1.1. Introduction
Welcome to the documentation of the Ansible Deployment for GNU Health!
The Ansible playbooks in this project aim to automatically deploy an hospital information system based on GNU Health and other free software. The main elements are:

HIS node: Hospital Information System, core of the GNU Health system (role and playbook just called gnuhealth)
Desktop: Workstation with the GNU Health client to access the HIS node

Thalamus: This is used to build up a GNU Health Federation which contains multiple HIS nodes (still in development)

Orthanc: The DICOM server is not directly part of the GNU Health system but its integration is provided

DHIS2: Health management information system (HMIS), platform for analyzing and reporting, often in a national scale (used for developping the interaction)
Using the playbooks you can easily install the servers - even distributed on multiple systems. Numerous configuration options are realized in order to ease and automize standard configuration steps.
Supported operating systems are the latest Debian, Ubuntu LTS and openSUSE Leap.
You can find the Ansible repository and the repository of this documentation on Codeberg.
1.2. Installation vs. Administration
This repository contains automated solutions with various configuration options for installation and administration procedures.
Installation refers to calling the playbooks with the _minimal suffix and keeping the default configuration as in the first example.
Administration means extending the functionality by system administration procedures like firewall, backup/restore, etc.
The installation is continuously tested for the latest Debian, Ubuntu LTS and openSUSE Leap. However the administration features are mainly developed, tested and used for Debian. For productive settings using various roles and configuration options it is currently recommended to use Debian.
FreeBSD was supported in the past but is discontinued. To reuse the old state just uncomment it in roles/check/vars/main.yml
1.3. Virtualization
The deployment of GNU Health and other applications is automated in a modular way. Thus the same scripts ca be used for an installation without virtualization, on one Virtual Machine (VM) or distributed on multiple VMs or system containers in order to have one distinct system per functionality. The biggest example that is automated in this project is visualized in the following graphics:
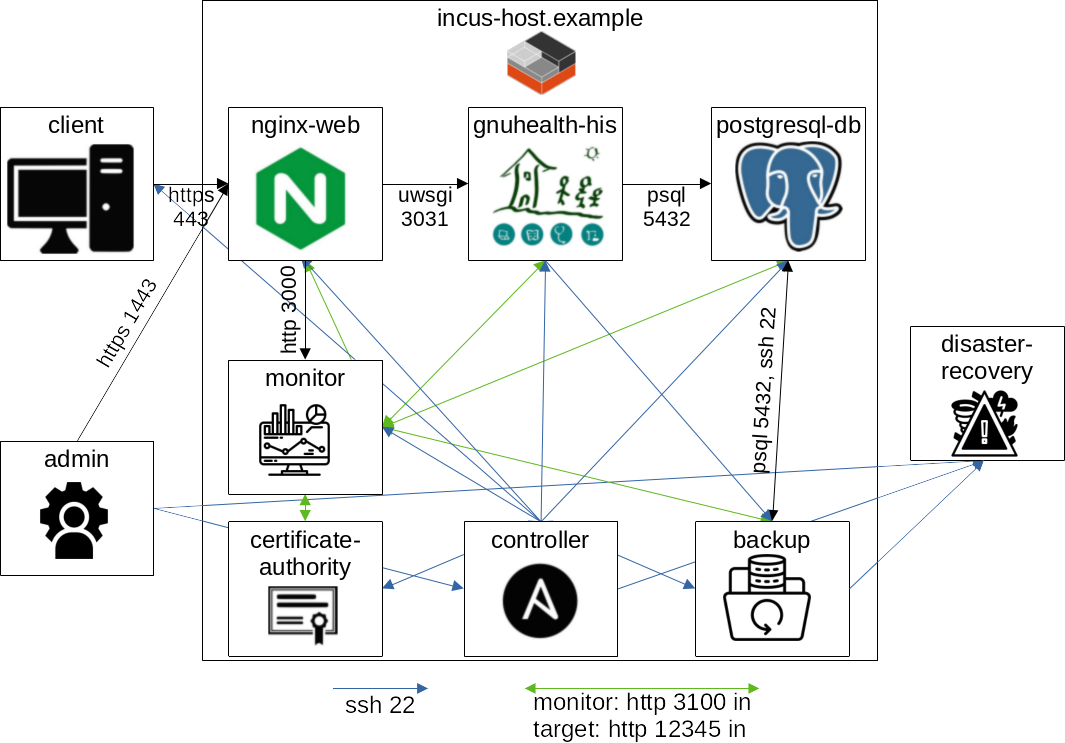
Example of separating every service into a distinct system
All this is realized using the automation and configuration management tool Ansible.
The project was developped with and intended for using VMs. While it is not functional for Docker containers e.g. because it is using systemd for GNU/Linux it does work well with Incus containers.
1.4. Directory structure
For every type of deployment there are .yml files in the playbooks directory. Those are the main scripts that you can execute.
Additionally there are Ansible roles with the corresponding names and other roles getting called implicitly. They are containing the tasks that will install packages and perform configuration steps for creating the desired service.
If files are needed by different systems those are put into the fetch folder. For some cases - e.g. handling certificates or SSH keys - files have to be transferred from one system to another. Besides the desktop systems having the GNU Health client installed need connection parameters of the server. Those are also written into this folder.
Finally there are tests which are described in detail later on.
You can modify ansible.cfg in the top level directory if you wish to change your Ansible configuration options.
1.5. Documentation structure
Any playbook or role in this project has a corresponding subchapter in the documentation. The Playbooks chapter rather gives a top level overview and the Roles chapters describes functionalities more in detail - even with a short description for every single variable.
For a quickstart you can switch directly into the chapter Examples.
Further chapters target questions of Security, System Administration and Project Information in detail.